This is an introduction to the Eurorack Flying Bus Cable.
This is a power distribution cable for Eurorack modular synthesizers. It's useful when your power supply has fewer sockets than the number of modules you want to connect. The cable features a stylish design with a black base color and gray markings for the -12V line.
This product is available in 5-connector and 9-connector versions and can be purchased below.
- Product Photos
- Flying Bus Cable Function
- Basic Usage
- Flying Bus Cables and Current Capacity
- About This Product's Development
- Product Specifications
Product Photos

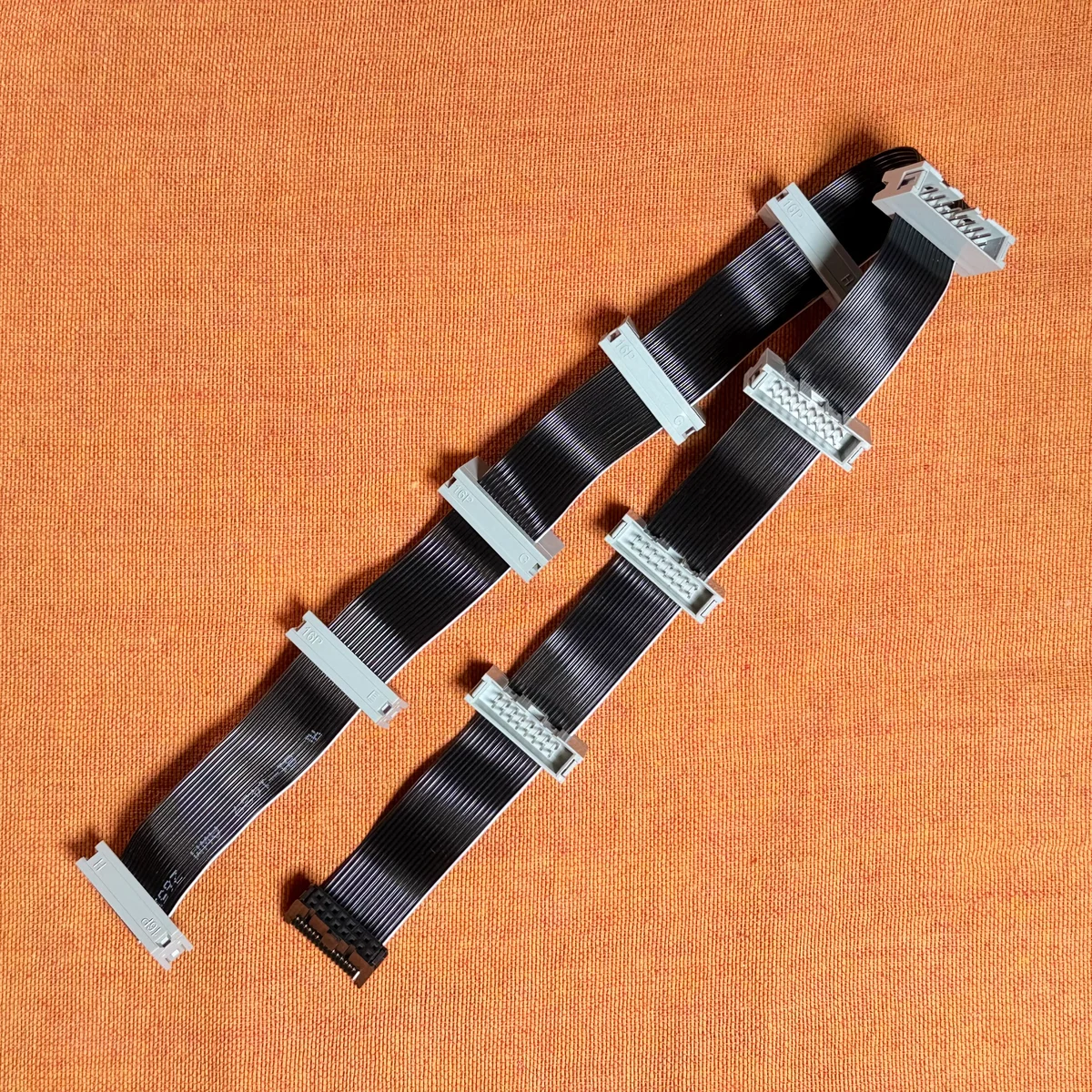

Flying Bus Cable Function
This flying bus cable distributes power from a power supply to multiple modules. In Eurorack modular synthesis, voltage from the mains is conditioned for module use and then distributed to each module.
Typically, a bus board (a PCB) is used for power distribution, but this flying bus cable enables more space-efficient and flexible wiring. It is particularly convenient for small cases or setups with fewer modules.
Basic Usage
This cable is designed to be used together with a separate power supply device. Please note that this cable alone cannot generate the voltage needed to power modules.
The flying bus cable is used by connecting one end's connector to a power supply and the branched connectors to individual modules. It is suited for extending cables from powered cases or power modules to distribute power to multiple modules.
Note: Please always connect and disconnect cables with the power turned OFF.
Flying Bus Cables and Current Capacity
A flying bus cable like this serves as an alternative to a bus board. In our shop, we carry the zudo-bus, a Takazudo-made bus board. Here's a brief look at the difference between such bus boards and flying bus cables.
Both Flying Bus Cables and Bus Boards Are Power Strips
First, both bus boards and flying bus cables are essentially like household power strips. They simply distribute the voltage from the power supply to each module's +12V, -12V, GND lines, etc. — a very simple circuit. In that sense, there's no fundamental difference in functionality. The key point is that flying bus cables use thinner copper wire, so when current draw is high, there's a possibility of heat generation or insufficient voltage reaching the modules.
The ribbon cable used in this flying bus cable is 28AWG, the standard gauge used in general Eurorack modular synthesizers — think of it as copper wire with a cross-section diameter of approximately 0.32mm. This is very thin wire, not suited for carrying large amounts of current. The reason such cables are used for power in Eurorack is apparently because the format adopted existing cable standards to keep costs down (Reference: Modular Profile: Dieter Doepfer | Sound On Sound).
Characteristics of Flying Bus Cables
A flying bus cable uses this thin cable to supply power to multiple modules. Because of this, caution is needed when some connected modules have higher power consumption. Think of this like how connecting too many appliances to a household power strip can be dangerous (Reference: How Things Work | Denjirou-sensei no Hapi-Ene!)
However, the voltage and current used in modular synths are far lower than what comes from a household outlet. So barring a short circuit, the risk of fire is extremely unlikely, but as a guideline, consider approximately 1A as the total current limit for a flying bus cable. What happens when pushing a flying bus cable to its limits depends on the module — for example, oscillators may have unstable pitch, or digital modules may repeatedly restart. If such symptoms occur, you may need to review your power setup. That said, if you experience such issues, the cause is more likely insufficient power supply output than the flying bus cable itself.
The topic has drifted slightly toward power supplies, but regarding flying bus cables specifically — when using a relatively large number of modules, you'll need to use multiple bus cables from the power supply. For example, TipTop Audio's uZEUS power module is designed to accommodate multiple flying bus cables, likely with this consideration in mind.
Characteristics of Bus Boards
Bus boards, on the other hand, remove the limitations of flying bus cables. The copper traces can be made much thicker, making problems from overdrawing unlikely. They also typically include minor noise-reduction circuitry. Additionally, some Eurorack bus boards include functionality to add +5V power. However, all of this depends on the bus board's design. And regarding noise reduction, since noise sources are varied, it shouldn't be taken as a guaranteed solution.
Which Should You Use?
In conclusion, for small-scale setups, flying bus cables are recommended for their cost and convenience. However, for large-scale setups, using a properly built bus board is advisable. For larger cases, having a fixed solution is also more practical.
For more detailed information about power and setup, I've written extensively in the following power supply beginner's guide articles.
- Eurorack Modular Synth Power Supply Guide (Part 1)
- Eurorack Modular Synth Power Supply Guide (Part 2)
- Eurorack Modular Synth Power Supply Guide (Part 3)
- Eurorack Modular Synth Power Supply Guide (Part 4)
About This Product's Development
This product was custom-manufactured by Takazudo Modular through a Taiwanese manufacturer. The manufacturer asked us to note that their cables are of higher quality than the typical Chinese products with inconsistent quality, so we're noting here that these are made in Taiwan.
Product Specifications
- 5-connector version: 1 input connector + 5 output connectors / approx. 30cm
- 9-connector version: 1 input connector + 9 output connectors / approx. 50cm
- 16-pin (2x8) connectors
- 28AWG 1.27mm pitch IDC Flat Ribbon Cable
That concludes our introduction of the Eurorack Flying Bus Cable.
We hope you find this helpful.